Integrated Trading International
The grading rules for American hardwood lumber were established over 100 years ago by the newly formed National Hardwood Lumber Association (NHLA). Today the NHLA has over 2000 members worldwide, and the NHLA rules are still the national standard for the US hardwood industry and form the basis for grading of export lumber.
Wood is a natural material and by its very nature may contain different characteristics and defects that need to be understood and allowed for in any given application. The grading of sawn wood into categories as it is processed helps to determine to a large extent the value and potential use possible or each board of sawn lumber.
The NHLA grading rules provide both the buyer and seller with a consistent language to use in specifying hardwood lumber transactions. Although the NHLA grading rules are targeted for the US marketplace, a reasonable knowledge is essential for buyers worldwide in order to attain their expected degree of quality. The grade of lumber purchased by a manufacturer will determine both the cost and waste factor that is achieved. Because the grades are based on the percentage of clear wood in the board, many of the beautiful, natural characteristics found in hardwoods are not considered in calculating the clear yield.
Hardwood lumber is usually graded on the basis of the size and number of cuttings (pieces) that can be obtained from a board when it is cut up and used in the manufacture of a hardwood product. The NHLA rules were designed with the furniture trade in mind to provide a measurable percentage of clear, defect-free wood for each grade. The upper grades provide the user with long clear pieces, while the Common grades are designed to be re-sawn into shorter clear pieces.
The upper grades, which will include FAS, FAS-One-Face (FAS/1F) and Selects, are most suitable for long clear mouldings, joinery products such as door frames, architectural interiors; and furniture applications, which require a heavy percentage of long wide cuttings.
The Common grades, primarily Number 1 Common (No. 1C) and Number 2A Common (No. 2AC), are likely to be most suitable for the kitchen cabinet industry, most furniture parts, and plank and strip flooring. Worth noting is the fact that once re-sawn, the cuttings obtained from the Common grades will be the same clear wood as the upper grades but in smaller (shorter and/or narrower) cuttings. The grade name simply designates the percentage of clear wood in the board, not the overall appearance.
The American hardwood temperate forest resource is the largest of its kind anywhere in the world, with a significant history of sustainability. Exploring the Common grades, where possible, is invaluable in achieving the most value both in lumber cost and yield. These efforts will also help to ensure the sustainability of the resource for generations.
AHEC Europe would like to thank the NHLA for their collaboration in producing this section.
These Standard Grades form the framework by which all American hardwoods are traded. It is important to note that between buyer and seller any exception to these rules is permissible and even encouraged. For a complete description of the NHLA grades, consult the NHLA's "Rules for the Measurement and Inspection of Hardwoods and Cypress".
Prime grade
This grade has evolved from the NHLA grade of FAS for the export market. It is square edged and virtually wane free. The minimum clear yield will be select and better with appearance being a major factor. Minimum size of the boards varies, depending on the species, region, and supplier.
FAS
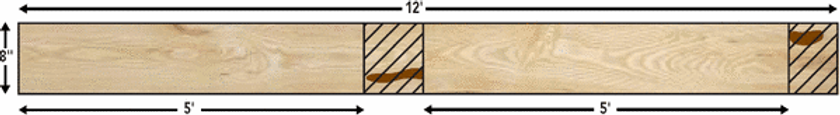
The FAS grade, which derives from an original grade "First And Seconds", will provide the user with long, clear cuttings - best suited for high quality furniture, interior joinery and solid wood mouldings. Minimum board size is 6" and wider and 8' and longer. The FAS grade includes a range of boards that yield from 83 1/3 % (10/12 ths) to 100% clear-wood cuttings over the entire surface of the board. The clear cuttings must be a minimum size of 3" wide by 7' long or 4" wide by 5' long. The number of these cuttings permitted depends on the size of the board with most boards permitting one to two. The minimum width and length will vary, depending on species and whether the board is green or kiln dried. Both faces of the board must meet the minimum requirement for FAS.
Note: Minimum yield 83 1/3 % clear wood cuttings on the poor face of the board.
FAS One Face (F1F)
This grade is nearly always shipped with FAS. The better face must meet all FAS requirements while the poor face must meet all the requirements of the Number 1 Common grade, thus ensuring the buyer with at least one FAS face. Often export shipments are assembled with an 80-20 mix, 80% being the percentage of FAS boards and 20% being the percentage of F1F boards. These percentages are strictly left to individual buyer and seller agreement.
Number 1 Common (No.1C)
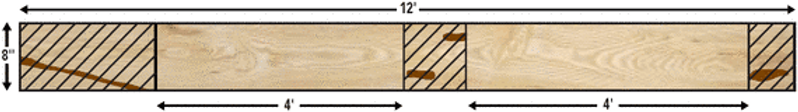
The Number 1 Common grade is often referred to as the Cabinet grade in the USA because of its adaptability to the standard sizes of kitchen cabinet doors used throughout the United States. Number 1 Common is widely used in the manufacture of furniture parts as well for this same reason. The Number 1 Common grades includes boards that are a minimum of 3" wide and 4' long and will yield clear face cuttings from 66 2/3 % ( 8/12 ths) up to, but not including, the minimum requirement for FAS (83 1/3 %). The smallest clear cuttings allowed are 3" by 3' and 4" by 2'. The number of these clear cuttings is determined by the size of the board. Both faces of the board must meet the minimum requirement for Number 1 Common.
Grading - An Introduction